Detailed instruction on building Vision Transformer models in LiBai¶
It’s easy for users to build the transformer-based models by using LiBai’s built-in layers. Let’s take a deep dive into the process of building a Vision Transformer model in LiBai.
Model Architecture¶
Vision Transformer was released in the paper An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
A Vision Transformer model contains three parts: Patch Embedding + Transformer Block + Linear Classification Head, which can be summarized in the following picture:
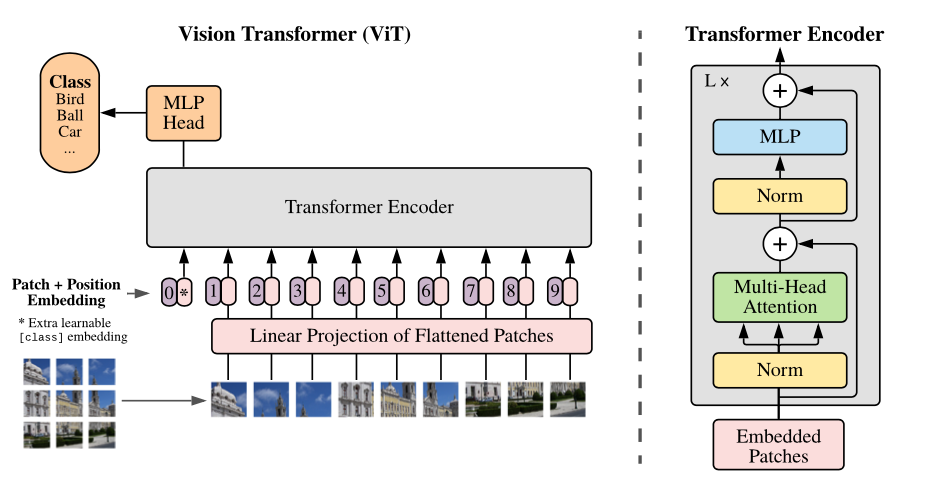
A simple Torch implementation of Vision Transformer¶
The following code shows the PyTorch implementation of ViT models modified from timm.models.vision_transformer:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_, PatchEmbed, Mlp, DropPath
"""
1. Build a self-attention module
"""
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0.0, proj_drop=0.0):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = (
self.qkv(x)
.reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads)
.permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
"""
2. Build a transformer block, which contains:
self-attention layer + mlp layer
"""
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
dim,
num_heads,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
qkv_bias=False,
drop=0.0,
attn_drop=0.0,
drop_path=0.0,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = Attention(
dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
proj_drop=drop,
)
# Use drop_path here
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0.0 else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(
in_features=dim,
hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer,
drop=drop,
)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
"""
3. Build a Vision Transformer model which contains three parts:
patch embedding + transformer block + mlp classification head
"""
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
in_chans=3,
embed_dim=192,
depth=12,
num_heads=3,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
drop_rate=0.0,
attn_drop_rate=0.0,
drop_path_rate=0.0,
num_classes=1000,
):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# patch embedding
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim
)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
# cls token and position embedding
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_embed = self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth decay rule
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)]
# transformer block
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[
Block(
dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=True, drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate, drop_path=dpr[i], norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, act_layer=nn.GELU)
for i in range(depth)])
# classification head
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim)
self.head = nn.Linear(embed_dim, num_classes)
# weight init
trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=0.02)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward_features(self, x):
# patch embedding
x = self.patch_embed(x)
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1)
# position embedding
pos_embed = self.pos_embed.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
x = self.pos_drop(x + pos_embed)
# transformer block
x = self.blocks(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x):
# only use cls token for classification
x = self.norm(x)
outcome = x[:, 0]
return self.head(outcome)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.forward_head(x)
return x
We have further decoupled the forward function into forward_features and forward_head:
forward_features: extract the image features using thepatch_embedlayer and a stack oftransformerblocksforward_head: take thecls_tokenof each sample and usenn.Linearfor classification
Implement 3D parallel Vision Transformer in LiBai¶
In this section, we will show users how to use libai.layers to build a 3D parallel Vision Transformer model with only 100+ lines of code, which is modified from libai.models.vision_transformer
Here is the LiBai implementation of Vision Transformer models, and users only need to replace the PyTorch modules with the corresponding libai.layers as follows:
# LiBai's implementation of Vision Transformer
import oneflow as flow
import oneflow.nn as nn
from flowvision.layers.weight_init import trunc_normal_
import libai.utils.distributed as dist
from libai.config.config import configurable
from libai.layers import LayerNorm, Linear, PatchEmbedding, TransformerLayer
"""
LiBai has already implemented:
1. PatchEmbedding Layer
2. Transformer Layer: Self-Attention + MLP + DropPath + LayerNorm
3. Linear Layer
We can directly build a Vision Transformer model with the built-in layers in LiBai as follows:
"""
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
in_chans=3,
embed_dim=192,
depth=12,
num_heads=3,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
drop_rate=0.0,
attn_drop_rate=0.0,
drop_path_rate=0.0,
num_classes=1000,
loss_func=None
):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# patch embedding
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbedding(
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
# cls token and position embedding with sbp signature
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(
flow.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim,
sbp=dist.get_nd_sbp([flow.sbp.broadcast, flow.sbp.broadcast]),
placement=dist.get_layer_placement(0),)
)
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(
flow.zeros(1, num_patches+1, embed_dim,
sbp=dist.get_nd_sbp([flow.sbp.broadcast, flow.sbp.broadcast]),
placement=dist.get_layer_placement(0),)
)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth decay rule
dpr = [x.item() for x in flow.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)]
# a stack of transformer block
ffn_size = int(embed_dim * mlp_ratio)
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(
*[
TransformerLayer(
hidden_size=embed_dim,
ffn_hidden_size=ffn_size,
num_attention_heads=num_heads,
attention_dropout_prob=attn_drop_rate,
output_dropout_prob=drop_rate,
drop_path_prob=dpr[i],
layer_idx=i,
)
for i in range(depth)
]
)
self.norm = LayerNorm(embed_dim, layer_idx=-1)
self.head = Linear(embed_dim, num_classes, layer_idx=-1)
# implement loss function in nn.Module to match LiBai style
self.loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() if loss_func is None else loss_func
# weight init function
trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=0.02)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward_features(self, x):
# patch embedding
x = self.patch_embed(x)
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(
x.shape[0], -1, -1
) # stole cls_tokens impl from Phil Wang, thanks
cls_token = cls_token.to_global(sbp=x.sbp, placement=cls_token.placement)
x = flow.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1)
# position embedding
pos_embed = self.pos_embed.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
pos_embed = pos_embed.to_global(sbp=x.sbp, placement=pos_embed.placement)
x = self.pos_drop(x + pos_embed)
# transformer block
x = self.blocks(x)
return x
def forward_head(self, x):
x = self.norm(x)
outcome = x[:, 0]
outcome = self.head(outcome)
return outcome
def forward(self, images, labels=None):
x = self.forward_features(images)
x = self.forward_head(x)
if labels is not None and self.training:
losses = self.loss_func(x, labels)
return {"losses": losses}
else:
return {"prediction_scores": x}
@staticmethod
def set_pipeline_stage_id(model):
dist_utils = dist.get_dist_util()
# Set pipeline parallelism stage_id
for module_block in model.modules():
# module.origin can get the original module
if isinstance(module_block.origin, PatchEmbedding):
module_block.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
elif isinstance(module_block.origin, TransformerLayer):
module_block.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(module_block.layer_idx)
# Set pos_embed and cls_token stage id
model.pos_embed.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.cls_token.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.pos_drop.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.norm.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
model.head.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
model.loss_func.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
Details about LiBai’s implementation of the Vision Transformer model¶
1. Replace nn.Module with libai.layers
LiBai has already implemented PatchEmbedding, TransformerLayer, Linear, LayerNorm layers, and users only need to replace the module in Torch Vision Transformer models to convert a Torch model into LiBai’s style:
Block->libai.layers.TransformerLayernn.Linear->libai.layers.Linearnn.LayerNorm->libai.layers.LayerNormPatchEmbed->libai.layers.PatchEmbedding
2. Manually set the SBP signature of cls_token and pos_embed
In order to fit different parallel modes in LiBai, users must manually set the SBP signature for all the parameters and buffers of those layers not implemented in LiBai, like cls_token and pos_embed in Vision Transformer:
import oneflow as flow
import oneflow.nn as nn
import libai.utils.distributed as dist
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(
flow.zeros(
1, 1, embed_dim,
sbp=dist.get_nd_sbp([flow.sbp.broadcast, flow.sbp.broadcast]),
placement=dist.get_layer_placement(0),
)
)
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(
flow.zeros(
1, num_patches+1, embed_dim,
sbp=dist.get_nd_sbp([flow.sbp.broadcast, flow.sbp.broadcast]),
placement=dist.get_layer_placement(0),)
)
The SBP signature returned by
dist.get_nd_sbp([flow.sbp.broadcast, flow.sbp.broadcast])means to broadcastcls_tokenandpos_embedacross each GPU group.
3. Use the to_global() function to update the SBP signature of cls_token and pos_embed during forward function
In forward function, cls_token and pos_embed will be expanded to fit the input size. For efficiency, we can use the to_global() function to match the cls_token and pos_embed SBP signature with the input SBP signature like this:
def forward_features(self, x):
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(
x.shape[0], -1, -1
)
# use to_global to update the sbp signature of cls_token
cls_token = cls_token.to_global(sbp=x.sbp, placement=cls_token.placement)
x = flow.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1)
# use to_global to update the sbp signature of pos_embed
pos_embed = self.pos_embed.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
pos_embed = pos_embed.to_global(sbp=x.sbp, placement=pos_embed.placement)
4. Manually set the stage id for pipeline parallel training
Most of the built-in layers in LiBai has the arg named layer_idx for pipeline parallel settings. To configure a 1F1B pipeline parallel model, users should manually set the stage id for each layers in the model, which will automatically assign different layers on different stages and insert buffer in the process of forward & backward computation for 1F1B pipeline parallel training. With the help of layer_idx, we can simply get a pipeline parallel Vision Transformer model like:
import libai.utils.distributed as dist
"""
This is a staticmethod for class inherited from nn.Module,
which uses module.origin to get the original module.
"""
@staticmethod
def set_pipeline_stage_id(model):
dist_utils = dist.get_dist_util()
# Set pipeline parallelism stage_id
for module_block in model.modules():
# module.origin can get the original module
if isinstance(module_block.origin, PatchEmbedding):
module_block.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
elif isinstance(module_block.origin, TransformerLayer):
module_block.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(module_block.layer_idx)
# Set pos_embed and cls_token stage id
model.pos_embed.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.cls_token.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.pos_drop.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(0)
model.norm.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
model.head.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
model.loss_func.config.stage_id = dist_utils.get_layer_stage_id(-1)
Manually set the stage id:
PatchEmbeddingshould be on the first stageAutomatically assign the stage for
TransformerLayerwithlayer_idxargscls_token,pos_embed,pos_dropshould be on the first stagenorm,headandloss_funcshould be on the last stage
Please see Write your own pipeline parallel model for more details about the settings of pipeline parallel training in LiBai.